MIR-4: High Level Architecture
| Author | Igor Rendulic |
|---|---|
| Status | Draft |
| Type | Architecture |
| Created | 2022-04-29 |
Table of Contents
Abstract
Mailio Architecture is aimed towards eventual decentralization and at the same time support the same functionalities as currently available on https://mail.io.
Motivation
Mailio Handshake feature is one of the main reasons for creation of Mailio. A slogan - Pollution Control for Unwanted Email did not fully live up to it’s name, where receiving emails is based on inclusivity (priority for pre-approved senders) vs exclusivity (e.g. reporting spam, unsubscribing, …).
The efficient implementation proved difficult, if not impossible on SMTP protocol. Handshakes were based on autoresponders which lead to overwhelming bounce rates and reputation problems even when sending practices were spotless. There was also a problem with human component - people are nowadays very wary to click on automated email.
This architecture aims to address those problems and deliver true Pollution Control for Unwanted Emails.
High Level Architecture
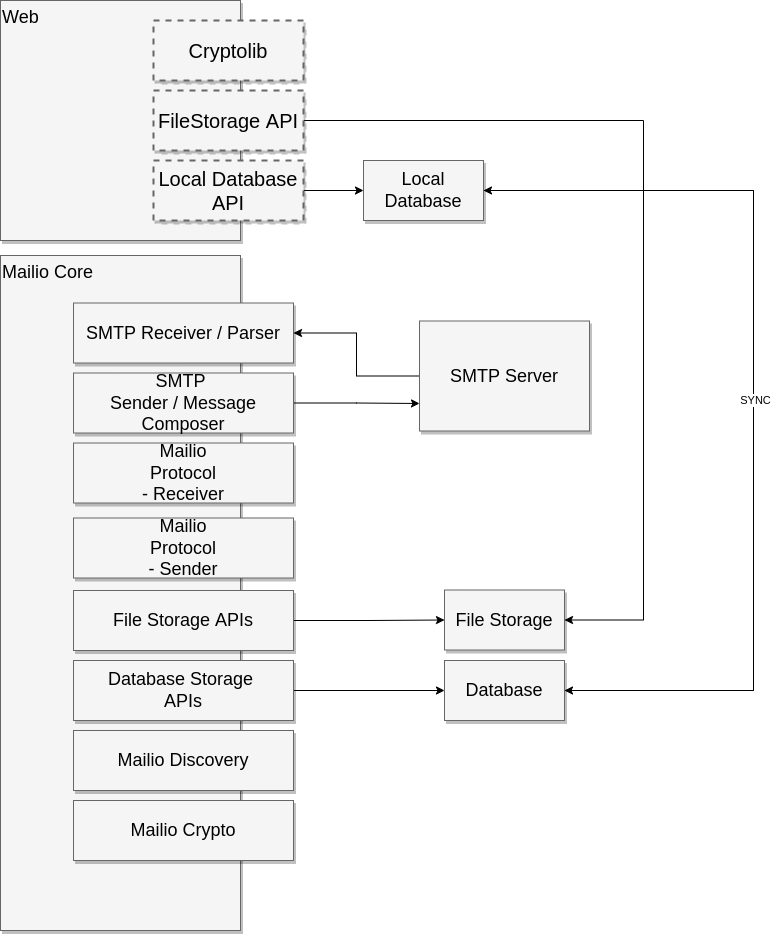
Design Goals
- Replicability
- Interoperability
- Low latency
- Reliability
- Fault tolerance
Service dependencies
These are external software solution required for to run Mailio. Decisions are made based on what worked well on https://mail.io or what could improve the architecture.
Local Database
It’s important to keep users messages in sync. For that we need a database that sync really well.
Technologies to assess:
SMTP Server
Postal is a complete and fully featured mail server for use by websites & web servers.
File Storage
- S3 compatible storage
Message Queue
- RabbitMQ message broker
Web Specification
Image depicts high level Mailio architecture. Mailio is highly modularized. This is a design concept allowing us to upgrade and most importantly test the components separately and independently. It also accomodates less friction when parallel upgrades are in motion.
Selected language: Typescript
Cryptolib
Cryptology library compatible with ECDSA algorithms:
Library need to be turned into framework agnostic library before it can be used.
FileStorage API
Due to the nature of ownership of contents of the individual messages there must be direct access to the file storage:
Library need to be turned into framework agnostic library before it can be used.
Local Database API
- PouchDB as already mentioned PouchDB is chosen for its syncing abilities.
Along with credible sync there is no need to perform queries over the network as PouchDB resides inside the browser and thus it makes it extremely faster. This comes in handy for search over decrypted data which can be in readable form only on users computer and not on any other hardware.
It stores data locally using IndexedDB and WebSQL in the browser.
Core Mailio Specification
Core Mailio is a backend server written in Go
SMTP Receiver / Parser
Building an email integration with Postal and parsing raw MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail Exception) as defined by applicable RFCs with Gmime Golang wrapper go-mime
SMTP Sender / Message Composer
Building an email integration with Postal and creating raw MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail Exception) as defined by applicable RFCs with Gmime Golang wrapper go-mime
Mailio Protocol Receiver
Building an email message parser for inner Mailio server communication over HTTP. The specification is subject to separate MIR (undefined at the moment of writing).
Mailio Protocol Sender / Message Composer
Building an email message creator for inner Mailio server communication over HTTP. The specification is subject to separate MIR (undefined at the moment of writing).
File Storage APIs
Integration with S3 compatible storage:
Database Storage APIs
Implementation and interface for database operations with:
Mailio Discovery
Implementation of DNS discovery mechanism and identification of the type of server (SMTP vs Mailio)
Mailio Crypto
Mailio frontent/web compatible/ECDSA/AES compatible cryptology library:
TBD: Move the library to mailio repository
Rationale
The rationale fleshes out the specification by describing what motivated the design and why particular design decisions were made. It should describe alternate designs that were considered and related work, e.g. how the feature is supported in other languages.
Reference Implementation
An optional section that contains a reference/example implementation that people can use to assist in understanding or implementing this specification. If the implementation is too large to reasonably be included inline, then consider adding it as one or more files in ../assets/mir-####/.
Security Considerations
All MIRs must contain a section that discusses the security implications/considerations relevant to the proposed change. Include information that might be important for security discussions, surfaces risks and can be used throughout the life cycle of the proposal. E.g. include security-relevant design decisions, concerns, important discussions, implementation-specific guidance and pitfalls, an outline of threats and risks and how they are being addressed. MIR submissions missing the “Security Considerations” section will be rejected. An MIR cannot proceed to status “Final” without a Security Considerations discussion deemed sufficient by the reviewers.
Copyright
Copyright and related rights waived via CC0.
Citation
Please cite this document as:
Igor Rendulic, "MIR-4: High Level Architecture [DRAFT]," Mailio Improvement Proposals, no. 4, April 2022. [Online serial]. Available: https://mirs.mail.io/MIRS/mir-4.